People with smartphones can be said as “Augmented Humans” with augmented intelligence. However, due to the limited rationality[1] described by H. Simon, information is not always accepted as intended by the sender. Even if it is accepted, it does not necessarily lead to behavioral change. Such bounded rationality that keeps individuals at the local minimum is unhealthy for the smart society. To design environmental intelligence as a spatial information system and to make symbiotically relationship for people with its environment and information devices, it is necessary to develop strategies for presenting information based on the principles of human, that can only possess bounded rationality.
Therefore, this research aims to create a technological foundation , design theories and guidelines to realize interactions that beyond human bounded rationality in a smart city and to achieve social wellbeing (Fig. 1). The specific goal is to improve people’s health, safety, convenience, and enjoyment in a smart city, which is also an information space that comprehensively contains dynamic information throughout the city. To beyond the three limitations of bounded rationality[2] such as the limitation of rationality, the limitation of outreach and the limitation of vision) in a smart city, we are going to build an interaction infrastructure that supports the process of deciding the optimal action from information (Research Subject 1: Interaction of Awareness), the process of distributing information to the city (Research Subject 2: Human City Interaction with non-human like robots ), and the process of acquiring correct information from the city (Research Subject 3: Interaction of Expanding Perspective). This research will enable people with expanded intellectual rationality to acquire information on health, safety and disaster prevention, and amplifying enjoyment from the huge information space and behave optimally, which will result in extending healthy life expectancy, reducing traffic accidents, coping with large-scale disasters. Moreover, it can greatly promote the wellbeing of society.
[1] Simon, H. A. (2013). Administrative behavior. Simon and Schuster.
[2] 塩沢由典(1990)『市場の秩序学』筑摩書房、第11章「複雑系における人間行動」

Research Subjects
-
Research Subject 1: Interaction of Awareness
Nakazawa Group There are moments when people need information. For example, when an action is needed to escape a crisis, or when an action is needed to maintain health, or when an action to have fun. People may or may not know that such behaviors exist. To address these issues, researchers specializing in information systems,…
-
Research Subject 2: Human City Interaction with non-human like robots
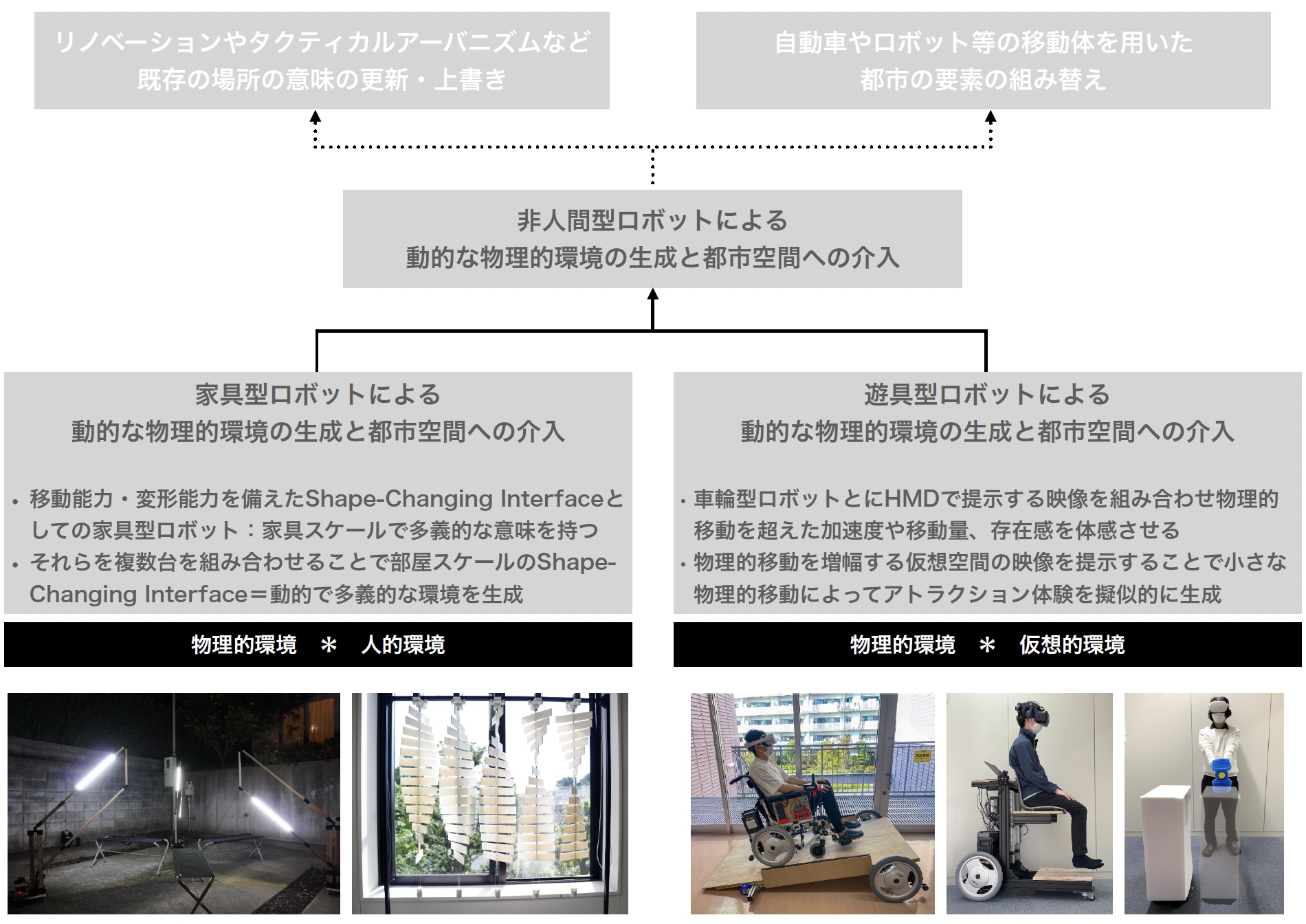
Yasuto Nakanishi Group The environment in which people live influences their behavioral patterns and unconscious thoughts. When I moved from the Nara to Tokyo upon entering university, I was initially concerned about the lack of mountains in my surroundings. My friend from Funabashi, a flat area by the sea, disliked the hills around her university…
-
Research Subject 3:Analyzing and Visualizing Human Society Interaction
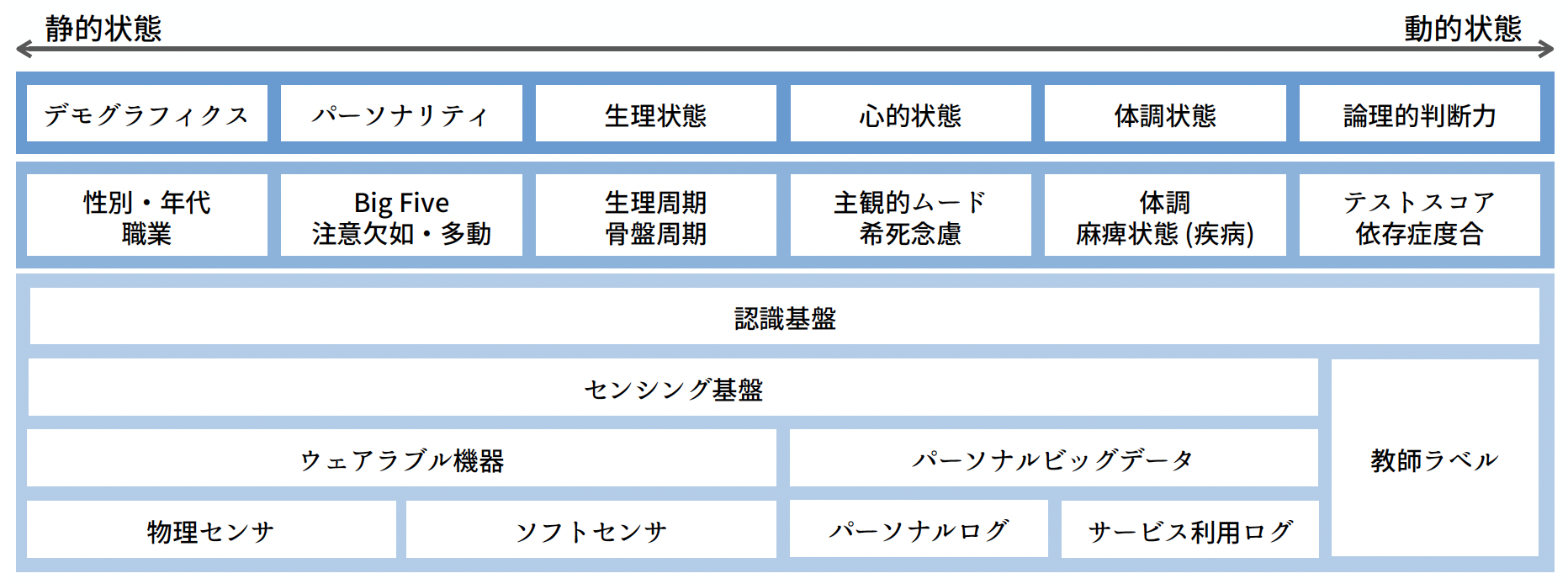
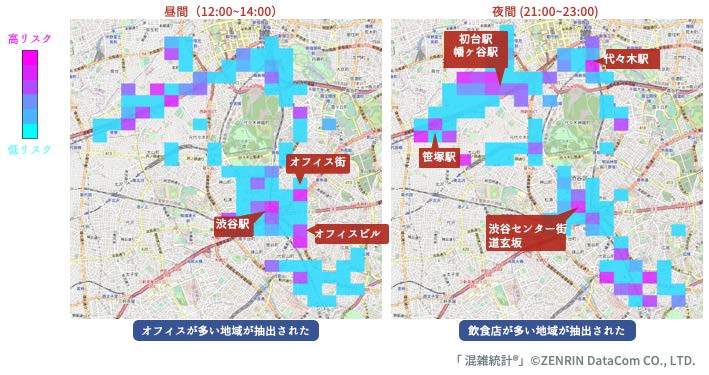
Toyoda Group The emergence of a large and comprehensive data on cities and SNSs allows people to expand their horizon. Our goal is to develop methods for decision making based on information analysis and visualization of the large-scale data, and fundamental technologies for personalized information presentation. We develop information analysis and visualization methods through several…
Projects
-
Exploratory Model Analysis Using Data-Driven Neuron Representations
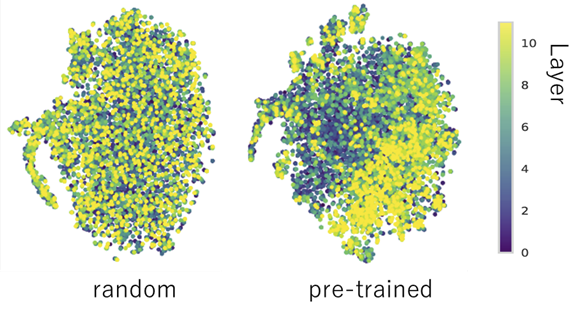
Probing classifiers have been extensively used to inspect whether a model component captures specific linguistic phenomena. This top-down approach is, however, costly when we have no probable hypothesis on the association between the target model component and phenomena. In this study, aiming to provide a flexible, exploratory analysis of a neural model at various levels…
-
Analyzing Political Polarization on Microblogs with Social Network Segregation and Users’ Political Leanings
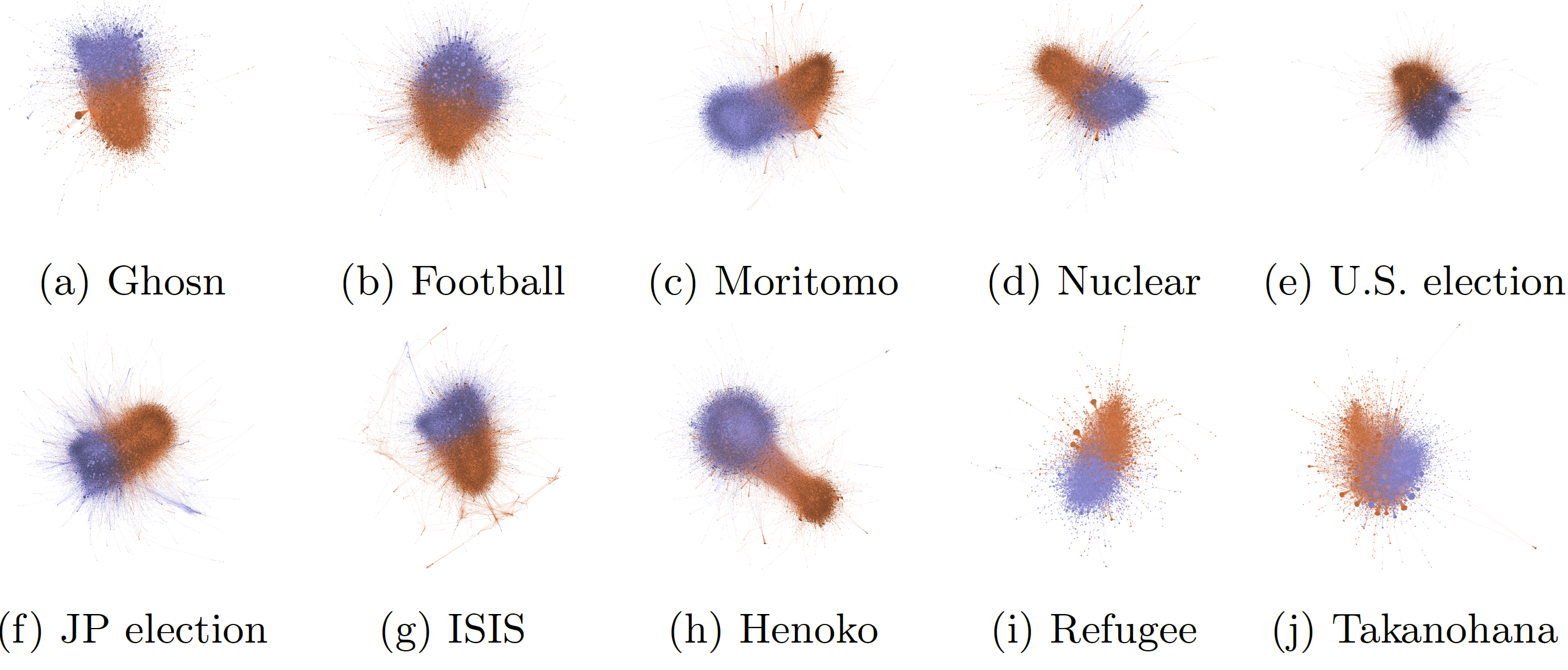
Political polarization on microblogs has been studied in terms of the user interaction between partisans and across partisan lines, such as echo chamber effects and the cross-ideological information diffusion.Although previous studies imply that politically neutral users might mediate the discussions, it has not been examined how the overall cross-ideological interactions are taken place by politically…
-
Diachronic Analysis of Users’ Stances on COVID-19 Vaccination in Japan using Twitter
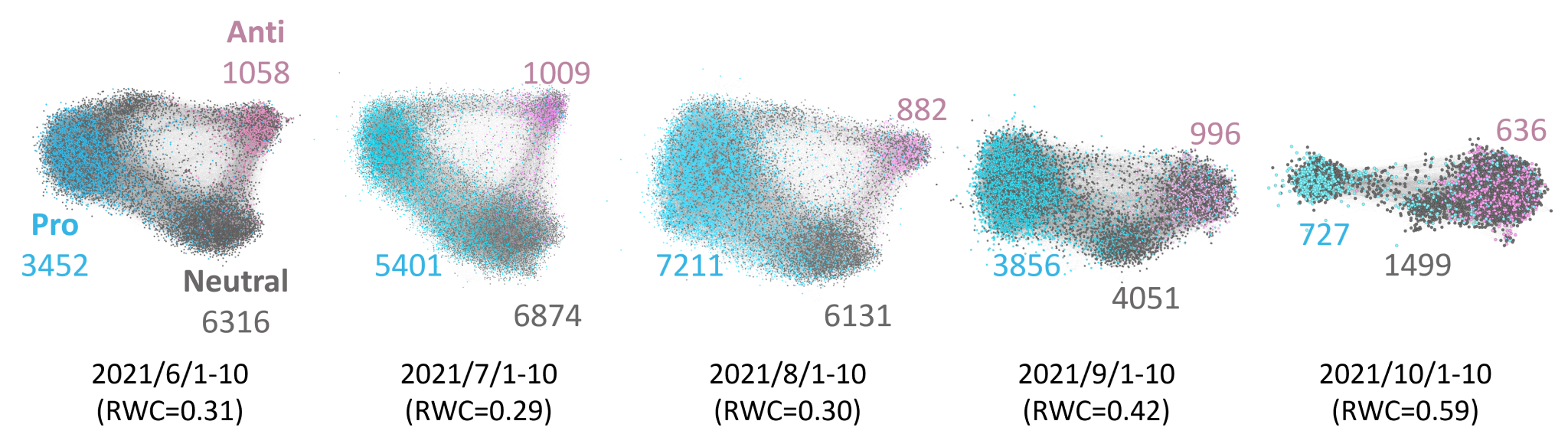
To prevent and curb viral outbreaks such as COVID-19, it is important to increase vaccination coverage whileresolving vaccine hesitancy and refusal. To understand why COVID-19 vaccination coverage had rapidly increased in Japan, we analyzed Twitter posts (tweets) to examine the evolution of people’s stance on vaccination and clarify the factors of why people decide to…
-
Boomshin
We proposed “Boomshin”, which uses an encounter-type tactile display to temporally switch between the presence and absence of tactile presentation of objects in space. We named the objects without tactile presentation as “Boomshin” and evaluated changes in the impression of the game experience by using the temporal appearance patterns of both as independent variables. The…
-
AmplifiedCarousel
With the spread of virtual reality (VR) attractions, vector generation techniques that enhance the sense of realism are gaining attention. Additionally, mixed reality (MR) at- tractions, which overlay VR onto a real-world display, are expected to become more prevalent in the future. However, with MR, it is impossible to move all the coordinates of the…