Cross-modal retrieval based on subjective information aims to enable flexible media retrieval services, such as allowing users to specify, for example, a text or/and an image to search audio clips. The resulting audio clips should have an impression similar to the specified text/image. Existing methods focus on building cross-media cross-modal relationships using objective information from the media, such as a movie image and its accompanying audio clip or an image and its accompanying caption. However, such a relation can be built only between the pieces of media that are originally related, which limits the flexibility of cross-modal media retrieval.
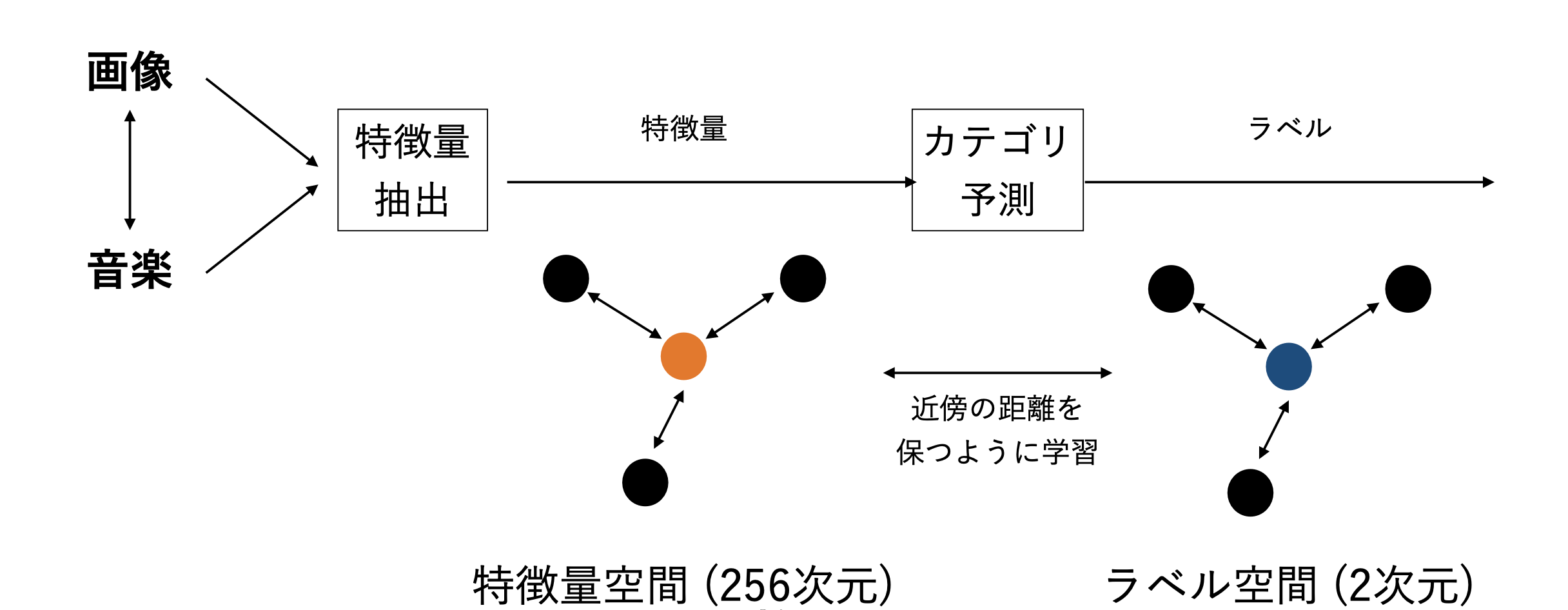
Instead of the objective information, this research leverages subjective information in the media clips for the similarity calculation to achieve more flexibility. This research pro- poses a novel cross-modal stochastic neighbor embedding technique called c-SNE. c-SNE can extract features on subjective information from pieces of media and map them in the common embedding space. It is a learning technique to bridge the heterogeneous gap between the modal distributions using label-weighted SNE. This allows users to find the media that share the same subjective information with a query medium. Our experiment results on the benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed method effectively performs in cross-modal distribution alignment and retrieval.