To prevent and curb viral outbreaks such as COVID-19, it is important to increase vaccination coverage while
resolving vaccine hesitancy and refusal. To understand why COVID-19 vaccination coverage had rapidly increased in Japan, we analyzed Twitter posts (tweets) to examine the evolution of people’s stance on vaccination and clarify the factors of why people decide to vaccinate. We collected all Japanese tweets
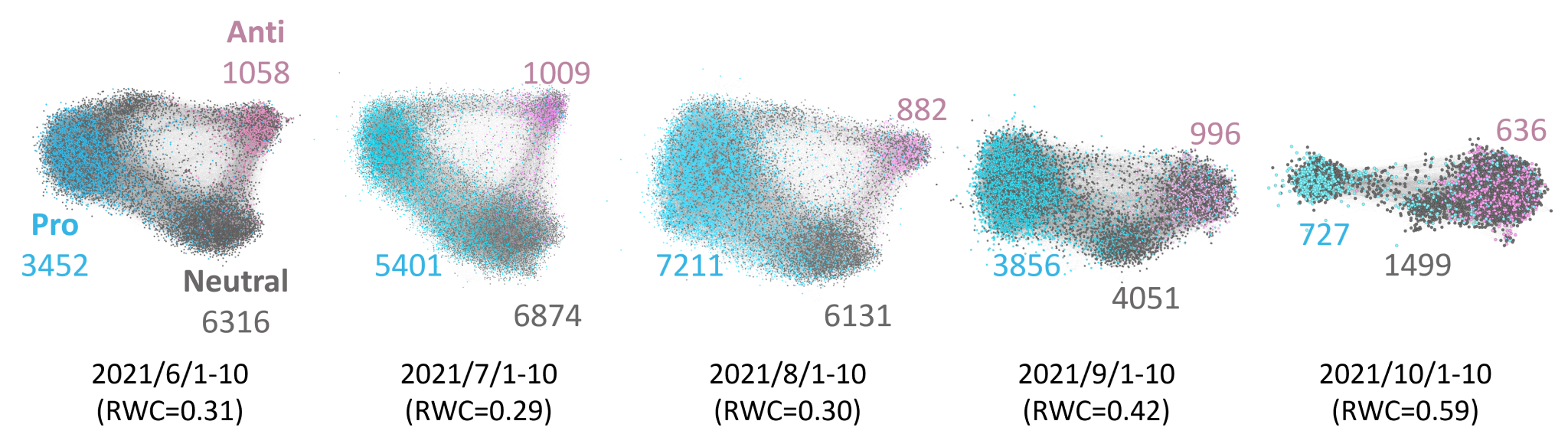
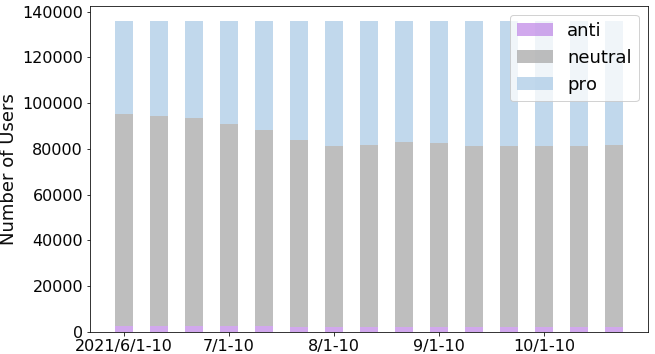
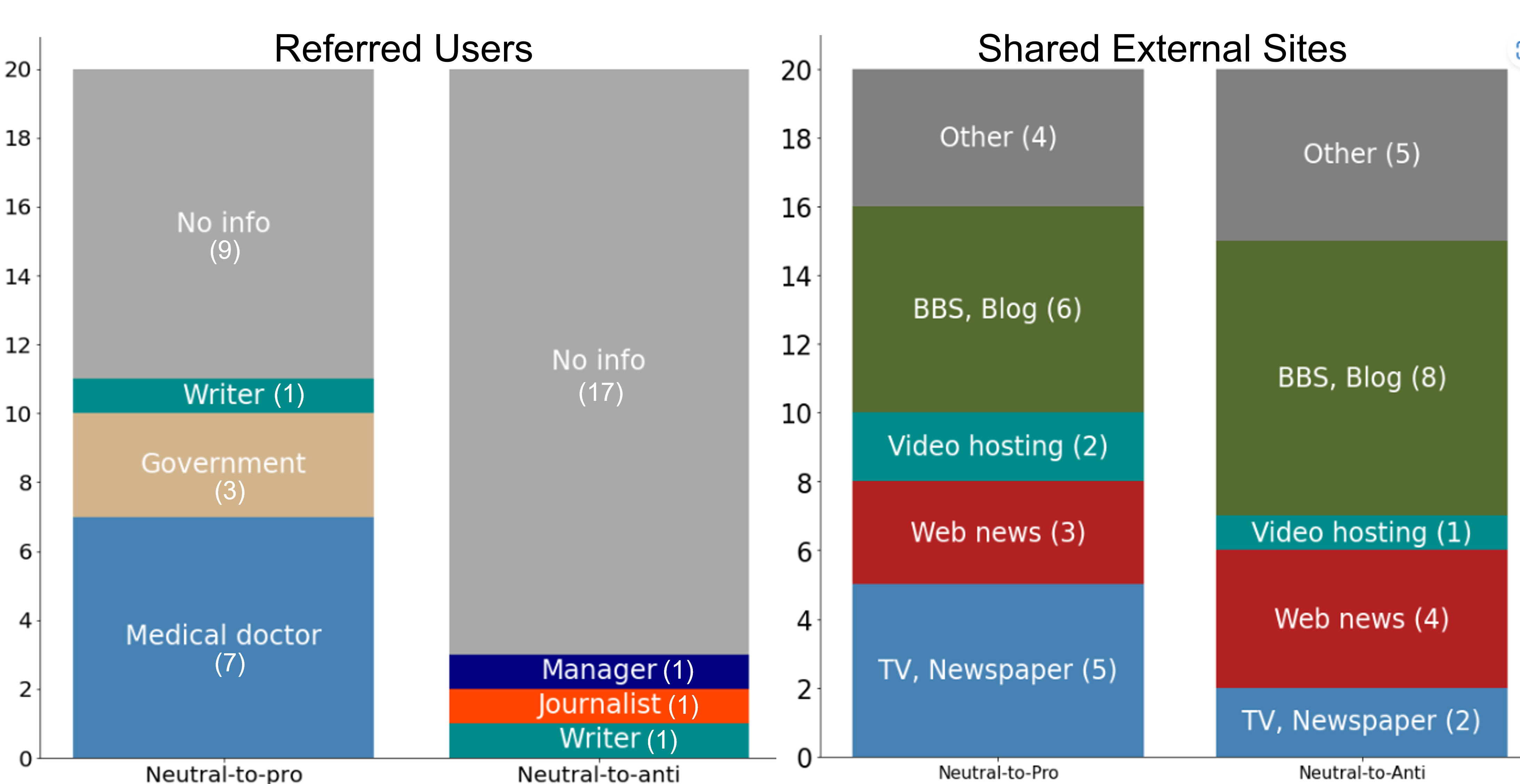
related to vaccines over a five-month period, and classified the vaccination stances of people who posted those tweets by using a deep neural network. Examining diachronic changes in the users’ stances on this large-scale vaccine dataset, we found that a certain number of neutral users changed to a pro-vaccine stance while very few changed to an anti-vaccine stance in Japan. Investigation of their information-sharing behaviors revealed what types of users and external sites were referred to when they changed their stances. These findings will help increase coverage of booster doses and future vaccinations.
Publication
- Shohei Hisamitsu, Sho Cho, Masashi Toyoda, Naoki Yoshinaga, Hongshan JIn, Diachronic Analysis of Users’ Stances on COVID-19 Vaccination in Japan using Twitter, ASONAM 2022 (to be appeared), 2022